Light, Reflection, and Refraction: Image
Steve Beeson, Arizona State University
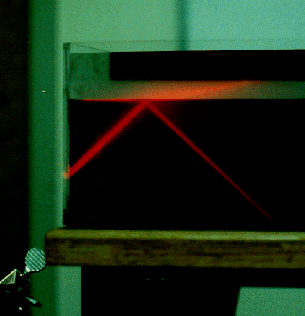
If we increase the incident angle of the laser (so that it's more nearly parallel to the surface) we see that the refracted angle also gets closer to parallel. (You can barely see the refracted beam in the thin layer of fog above the water surface).
What might happen if we go the other way and bring the incident beam nearer to normal (perpendicular) to the surface?
Go here if you want to see both images side by side.
 Return to the Total Internal Reflection Page
Return to the Total Internal Reflection Page
 Modules
Modules
 Light & Optics
Light & Optics
 Submodule 1
Submodule 1
 Readings
Readings
 PiN Homepage
PiN Homepage
 ACEPT
ACEPT
 Glossary
Glossary
 Help
Help
 Submodule 1 Page
Submodule 1 Page