Objectives:
|
|
Vocabulary:
|
Tree Diagram Summary
1. Conditional probabilities start at their condition.
2. Nonconditional probabilities start at the beginning of the tree.
3. Multiply when moving horizontally across a limb.
4. Add when moving vertically from limb to limb.
Possible
Classroom Examples:
- In a newspaper poll concerning violence on television, 600 people were asked, "What is your opinion of the amount of violence on prime-time television -- is there too much violence on television?". Their responses are summarized in the table below.
| Yes |
No |
Don't Know |
Total |
|
| Men |
162 |
95 |
23 |
280 |
| Women |
256 |
45 |
19 |
320 |
| Total |
418 |
140 |
42 |
600 |
- Cards are dealt from a full deck of 52. Find the probability of each of the given events.
- the first card is a diamond
- the second card is a spade, given that the first card was a diamond
- the first card is a diamond and the second card is a spade
- draw a tree diagram illustrating this
- Five cards are dealt from a full deck. Find the probability that the last four are spades, given that the first was a spade.
- A personal computer manufacturer buys 38% of its chips from Japan and the rest from America. 1.7% of the Japanese chips are defective, and 1.1% of the American chips are defective.
- Find the probability that a chip is defective and made in Japan.
- Find the probability that a chip is defective and made in America.
- Find the probability that a chip is defective.
- Find the probability that a chip is defect-free.
| Hearts
– Red |
Diamonds – Red |
| Clubs
– Black |
Spades
– Black |
Sample
Space of Rolling a Pair of Dice
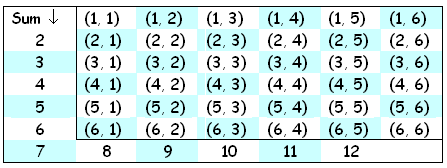
© 2007 Elizabeth E. K. Jones and the ASU
Department of
Mathematics and Statistics - All rights reserved.